Predicting the Future: Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025
Predicting the Future: Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Predicting the Future: Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Predicting the Future: Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025
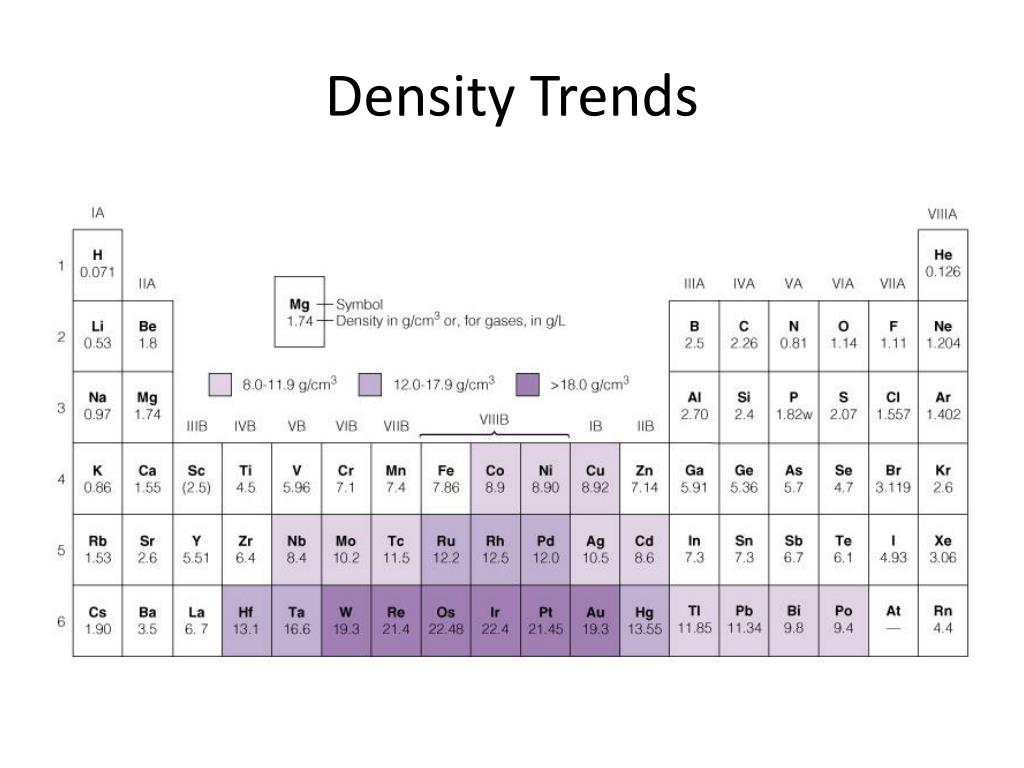
The periodic table, a fundamental tool in chemistry, is not merely a static arrangement of elements. It is a dynamic map reflecting the intricate relationships between elements, their properties, and their behavior. Within this framework, density trends play a pivotal role in understanding the physical nature of elements and their potential applications.
Understanding Density Trends
Density, a measure of mass per unit volume, is a fundamental physical property of matter. It is influenced by several factors, including:
- Atomic Mass: Heavier elements generally possess higher densities as they contain more protons and neutrons within their nuclei.
- Atomic Radius: Smaller atoms pack more tightly, leading to higher densities.
- Crystal Structure: The arrangement of atoms in a solid significantly impacts density.
- Interatomic Forces: Stronger interatomic forces result in denser materials.
Density Trends in the Periodic Table: A General Overview
As we move across a period (from left to right) in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases due to an increase in the effective nuclear charge. This leads to an increase in density.
Conversely, as we move down a group (from top to bottom), the atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells. Consequently, density generally decreases down a group.
Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025: A Look Ahead
While the fundamental principles governing density trends remain constant, several factors can influence their specific manifestation by 2025:
- Technological Advancements: Developments in material science, nanotechnology, and high-pressure synthesis could lead to the creation of novel materials with unprecedented densities.
- Discovery of New Elements: The possibility of synthesizing new elements beyond those currently known could introduce new densities and alter the existing trends.
- Environmental Concerns: The growing emphasis on sustainable materials and resource efficiency may influence research and development efforts towards denser materials with enhanced properties.
The Importance of Density Trends
Understanding density trends is crucial for various applications, including:
- Materials Science: Density is a key parameter in designing materials for specific applications, such as aerospace, construction, and electronics.
- Chemistry: Density trends inform the behavior of elements in chemical reactions and their ability to form compounds.
- Physics: Density plays a critical role in understanding the properties of matter, including its behavior under pressure and temperature.
- Geochemistry: Density trends are essential for understanding the composition and structure of the Earth’s crust and mantle.
Exploring Related Searches
1. Density of Elements in the Periodic Table:
This search explores the density values of individual elements in the periodic table, providing a comprehensive database of density data. It allows for comparisons between elements and the identification of trends across periods and groups.
2. Density of Metals in the Periodic Table:
Metals are known for their high densities due to their strong interatomic forces and close packing of atoms. This search focuses on the density trends within metallic elements, highlighting their unique properties and applications.
3. Density of Nonmetals in the Periodic Table:
Nonmetals exhibit a wide range of densities, from gases like helium to solids like carbon. This search investigates the density trends within nonmetals, emphasizing their diverse properties and applications.
4. Density Trends in the Periodic Table by Period:
This search examines density trends across each period in the periodic table. It highlights the systematic increase in density as we move from left to right, explaining the underlying factors responsible for this trend.
5. Density Trends in the Periodic Table by Group:
This search explores density trends down each group in the periodic table. It explains the general decrease in density as we move down a group, emphasizing the impact of increasing atomic radius on density.
6. Density of Isotopes in the Periodic Table:
Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but differ in their number of neutrons. This search investigates the impact of varying neutron numbers on density, highlighting the subtle differences in density between isotopes.
7. Density of Alloys in the Periodic Table:
Alloys are mixtures of metals, often exhibiting enhanced properties compared to their constituent elements. This search explores density trends in alloys, highlighting the importance of composition and microstructure in determining density.
8. Density of Compounds in the Periodic Table:
Compounds are formed by the chemical combination of elements. This search explores the density trends in compounds, emphasizing the role of chemical bonding and molecular structure in determining density.
FAQs on Density Trends in the Periodic Table
1. What is the densest element in the periodic table?
The densest naturally occurring element is osmium (Os), with a density of 22.59 g/cm³. However, synthetically produced elements like hassium (Hs) and seaborgium (Sg) are predicted to have even higher densities.
2. What is the least dense element in the periodic table?
The least dense element is helium (He), a noble gas with a density of 0.1785 g/L at standard temperature and pressure. Its low density is attributed to its small atomic mass and weak interatomic forces.
3. How does density affect the properties of materials?
Density influences several properties of materials, including:
- Strength: Denser materials generally exhibit higher strength and hardness.
- Conductivity: Density plays a role in thermal and electrical conductivity, with denser materials often being better conductors.
- Melting Point: Denser materials generally have higher melting points due to stronger interatomic forces.
- Reactivity: Density can influence the reactivity of materials, with denser materials often being less reactive.
4. Can density be altered by external factors?
Yes, density can be altered by external factors, such as:
- Pressure: Increasing pressure can compress materials, leading to increased density.
- Temperature: Increasing temperature can expand materials, leading to decreased density.
- Phase Changes: Changing the state of matter (solid, liquid, gas) can significantly alter density.
5. How are density trends used in everyday life?
Density trends are used in numerous everyday applications, including:
- Construction: Density is a crucial factor in selecting materials for building structures, ensuring stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Transportation: Density is important for designing vehicles, considering factors like fuel efficiency and weight distribution.
- Manufacturing: Density plays a role in choosing materials for various manufacturing processes, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Tips for Understanding Density Trends
- Visualize the Periodic Table: Use a periodic table with color-coded density values to visualize the trends across periods and groups.
- Focus on Atomic Structure: Understand the relationship between atomic mass, atomic radius, and density.
- Consider Interatomic Forces: Recognize how strong interatomic forces contribute to higher densities.
- Explore Real-World Examples: Look for examples of how density trends are applied in various fields, such as materials science and engineering.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of advancements in material science and the discovery of new elements, which can impact density trends.
Conclusion
Density trends in the periodic table provide a fundamental framework for understanding the physical properties of elements and their potential applications. While these trends are governed by basic principles, ongoing research and technological advancements may lead to new insights and applications. By understanding density trends, we can unlock the potential of elements and materials, shaping the future of science and technology.

/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
/periodictrendstable-5c4a46614cedfd000187c5db.jpg)



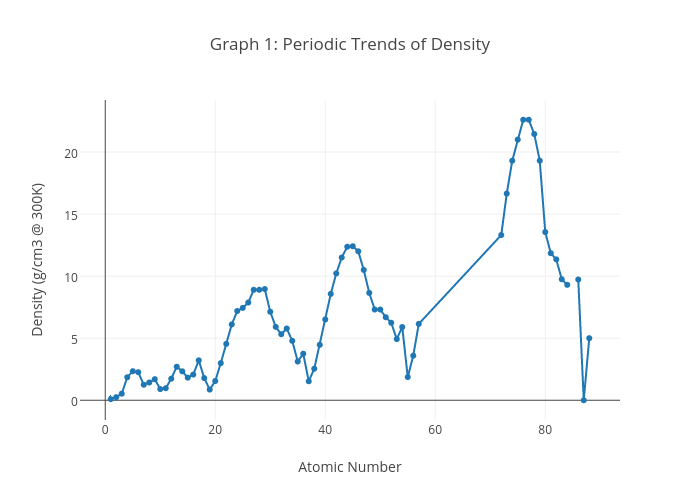
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Predicting the Future: Density Trends in the Periodic Table by 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!