Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025
Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025
- 3.1 Understanding the Dynamics: Key Drivers of Viral Evolution
- 3.2 Emerging Threats: A Glimpse into the Future
- 3.3 Virus Trends in 2025: A Closer Look at Potential Scenarios
- 3.4 Related Searches:
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips for Mitigating Viral Threats:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025

The world of viruses is in constant flux, driven by factors such as human behavior, environmental changes, and the ever-evolving nature of pathogens themselves. Predicting the future of viral threats is a complex task, but by analyzing current trends and understanding the forces shaping the landscape, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges we may face in the coming years. This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview of potential virus trends in 2025, highlighting their significance and offering practical tips for mitigating risks.
Understanding the Dynamics: Key Drivers of Viral Evolution
Several key factors contribute to the ever-changing nature of viral threats:
- Human Population Growth and Movement: As the global population continues to rise and travel becomes increasingly frequent, the potential for new viruses to emerge and spread rapidly increases. Dense urban environments, where close proximity and frequent interactions are common, create fertile ground for viral transmission.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Shifting climate patterns and habitat loss disrupt ecosystems, creating new opportunities for viruses to spill over from animals to humans. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can also impact the spread of existing viruses.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria poses a significant threat, as it can complicate treatment for viral infections. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics contribute to this growing challenge, requiring a concerted effort to promote responsible antibiotic stewardship.
- Technological Advancements: While technology can be a powerful tool in combating viral threats, it also presents new challenges. For example, the rapid spread of misinformation online can hinder public health efforts and exacerbate existing anxieties. Additionally, the use of emerging technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 for gene editing raises ethical concerns regarding potential unintended consequences.
- Globalization and International Trade: The interconnectedness of the global economy facilitates the rapid movement of people, goods, and pathogens. The potential for viruses to travel long distances within a short timeframe increases the need for robust surveillance and response systems.
Emerging Threats: A Glimpse into the Future
While predicting the specific viruses that may emerge in 2025 is impossible, several trends suggest potential areas of concern:
- Zoonotic Spillovers: The majority of new human viruses originate from animals. As human encroachment on wildlife habitats continues, the risk of zoonotic spillovers is likely to increase. This includes viruses like Ebola, Nipah, and Hendra, which have already demonstrated their potential for devastating outbreaks.
- Antibiotic-Resistant Infections: The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a growing concern, as it can complicate treatment for viral infections. Superbugs that are resistant to multiple antibiotics pose a significant threat, particularly in healthcare settings.
- Viral Evolution and Adaptation: Viruses are constantly evolving, adapting to new hosts and environments. This can lead to the emergence of new strains that are more transmissible, virulent, or resistant to existing vaccines or treatments. Influenza, for instance, undergoes frequent mutations, requiring annual updates to vaccines.
- Emerging Technologies and Their Impact: The widespread use of artificial intelligence (AI), nanotechnology, and other advanced technologies could have unintended consequences for viral evolution and spread. For example, AI-powered systems could be used to design new viruses or to manipulate existing ones, raising ethical concerns about biosecurity.
Virus Trends in 2025: A Closer Look at Potential Scenarios
1. The Rise of Novel Zoonotic Viruses:
- Scenario: A previously unknown virus, originating from a bat species in Southeast Asia, jumps to humans, leading to a global pandemic.
- Significance: This scenario highlights the increasing risk of zoonotic spillovers, driven by factors such as deforestation, wildlife trade, and climate change. The potential for a novel virus to spread rapidly across the globe underscores the importance of early detection, surveillance, and rapid response systems.
- Impact: A pandemic of this nature could result in widespread illness, mortality, and economic disruption. It would also strain healthcare systems and require significant resources for vaccine and treatment development.
2. The Challenge of Antibiotic-Resistant Infections:
- Scenario: A highly contagious respiratory virus emerges, but treatment options are limited due to the widespread prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Significance: This scenario highlights the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance, which can complicate treatment for viral infections. It underscores the need for responsible antibiotic stewardship and the development of new antimicrobial therapies.
- Impact: The lack of effective treatments could lead to increased morbidity and mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations. It could also strain healthcare resources and necessitate the development of alternative treatment strategies.
3. The Evolution of Existing Viruses:
- Scenario: A new strain of influenza emerges, resistant to current vaccines and antiviral medications.
- Significance: This scenario demonstrates the constant evolution of viruses, which can render existing vaccines and treatments ineffective. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing surveillance and rapid vaccine development efforts.
- Impact: A highly transmissible and drug-resistant influenza strain could lead to a significant increase in illness and mortality, particularly among elderly and immunocompromised individuals. It would also require a rapid response to develop new vaccines and treatments.
4. The Role of Emerging Technologies:
- Scenario: A bioterrorist group uses AI-powered tools to design a highly contagious and deadly virus.
- Significance: This scenario highlights the potential risks associated with emerging technologies, particularly in the realm of biosecurity. It underscores the importance of ethical guidelines and robust safeguards to prevent misuse of these technologies.
- Impact: A bioterrorist attack using a genetically engineered virus could have catastrophic consequences, leading to widespread illness, mortality, and societal disruption. It would also require a coordinated international response to contain the outbreak and prevent further attacks.
Related Searches:
1. Emerging Infectious Diseases:
- This search explores the broader landscape of emerging infectious diseases, including both viral and bacterial threats. It examines the factors that contribute to their emergence and the strategies for prevention and control.
2. Antimicrobial Resistance:
- This search focuses specifically on the growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. It examines the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to this global health challenge.
3. Pandemic Preparedness:
- This search explores the strategies and resources needed to prepare for and respond to pandemics. It includes topics such as surveillance, vaccine development, public health communication, and international collaboration.
4. Viral Evolution and Adaptation:
- This search investigates the mechanisms by which viruses evolve and adapt to new hosts and environments. It examines the factors that drive viral evolution and the implications for vaccine development and treatment strategies.
5. Biosecurity and Biosafety:
- This search focuses on the ethical and practical considerations related to the responsible use of biotechnology. It examines the risks associated with the misuse of biotechnology, including the potential for bioterrorism, and the measures needed to ensure biosecurity.
6. Zoonotic Diseases:
- This search explores the transmission of diseases from animals to humans. It examines the factors that contribute to zoonotic spillovers and the strategies for preventing their occurrence.
7. Climate Change and Infectious Diseases:
- This search examines the relationship between climate change and the emergence and spread of infectious diseases. It explores how changing climate patterns can impact disease transmission and the potential for new viruses to emerge.
8. Public Health Communication:
- This search focuses on the role of effective communication in public health emergencies. It explores the challenges and strategies for communicating accurate and timely information to the public during outbreaks and pandemics.
FAQs:
1. What are the most likely sources of new viruses in 2025?
- The most likely sources of new viruses in 2025 will be zoonotic spillovers from animals, particularly from wildlife. As human encroachment on animal habitats continues, the risk of viruses jumping from animals to humans will increase.
2. How can we prepare for potential viral threats?
- Preparing for potential viral threats requires a multi-pronged approach, including:
- Surveillance and early detection: Investing in robust surveillance systems to identify emerging viruses and track their spread.
- Vaccine development: Developing and stockpiling vaccines for known and potential threats.
- Antiviral treatments: Researching and developing new antiviral drugs to treat viral infections.
- Public health communication: Ensuring clear and timely communication to the public about potential threats and preventative measures.
- International collaboration: Working with global partners to share information, resources, and expertise.
3. What is the role of technology in mitigating viral threats?
- Technology can play a crucial role in mitigating viral threats by:
- Surveillance and tracking: Using AI-powered systems to analyze data and identify emerging outbreaks.
- Vaccine development: Utilizing AI and other technologies to accelerate vaccine development.
- Treatment development: Developing new antiviral drugs and therapies using advanced technologies.
- Public health communication: Leveraging social media and other digital platforms to reach wider audiences with important health information.
4. What are the ethical considerations related to emerging technologies and viral threats?
- The use of emerging technologies in the context of viral threats raises important ethical considerations, including:
- Biosecurity: Ensuring that these technologies are not misused for malicious purposes, such as bioterrorism.
- Privacy: Protecting the privacy of individuals whose data is used for surveillance and tracking.
- Equity: Ensuring that the benefits of these technologies are accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location.
5. What can individuals do to protect themselves from viral threats?
- Individuals can take several steps to protect themselves from viral threats, including:
- Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands frequently, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals.
- Getting vaccinated: Staying up-to-date on recommended vaccines, including the flu vaccine.
- Staying informed: Following public health guidelines and staying informed about emerging threats.
- Supporting public health efforts: Advocating for policies that promote public health and support research into viral threats.
Tips for Mitigating Viral Threats:
- Promote responsible antibiotic use: Advocate for and practice responsible antibiotic stewardship to reduce the development of antibiotic resistance.
- Support global health initiatives: Contribute to organizations that work to improve global health security and pandemic preparedness.
- Stay informed about emerging threats: Follow credible sources of information about viral outbreaks and public health guidelines.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, cover coughs and sneezes, and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Get vaccinated: Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccines, including the flu vaccine.
- Support research and development: Encourage investment in research to develop new vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools for viral threats.
Conclusion:
The future of viral threats is uncertain, but by understanding the key drivers of viral evolution and the potential scenarios that may unfold, we can better prepare for the challenges ahead. A proactive approach that emphasizes surveillance, research, and public health communication is essential for mitigating the risks posed by emerging and evolving viruses. Through collaboration and innovation, we can build a more resilient world, better equipped to face the challenges of the future.

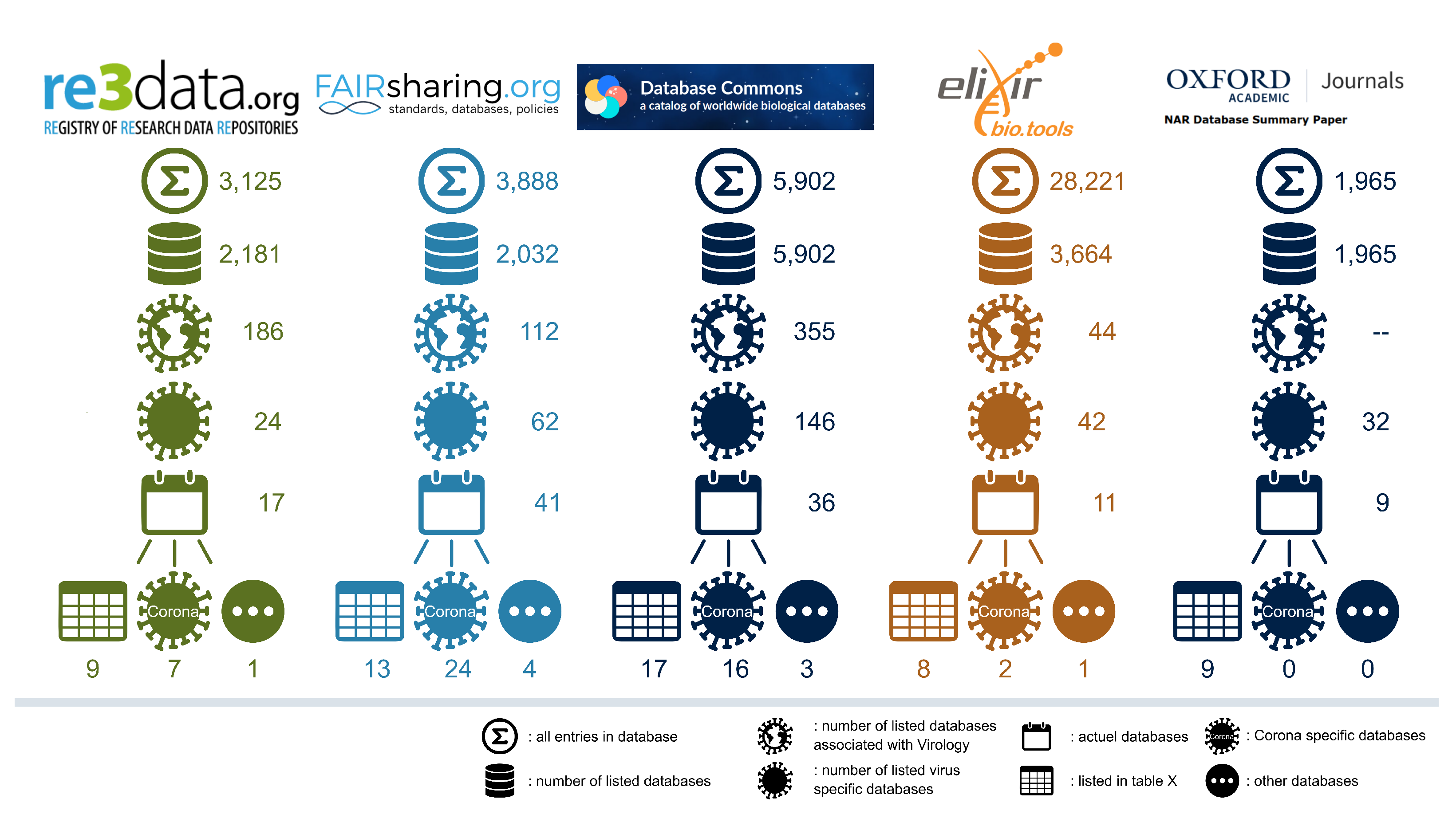






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Virus Trends in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!