Navigating the Economic Landscape: A Look at Inflationary Trends in 2025
Navigating the Economic Landscape: A Look at Inflationary Trends in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Economic Landscape: A Look at Inflationary Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Economic Landscape: A Look at Inflationary Trends in 2025
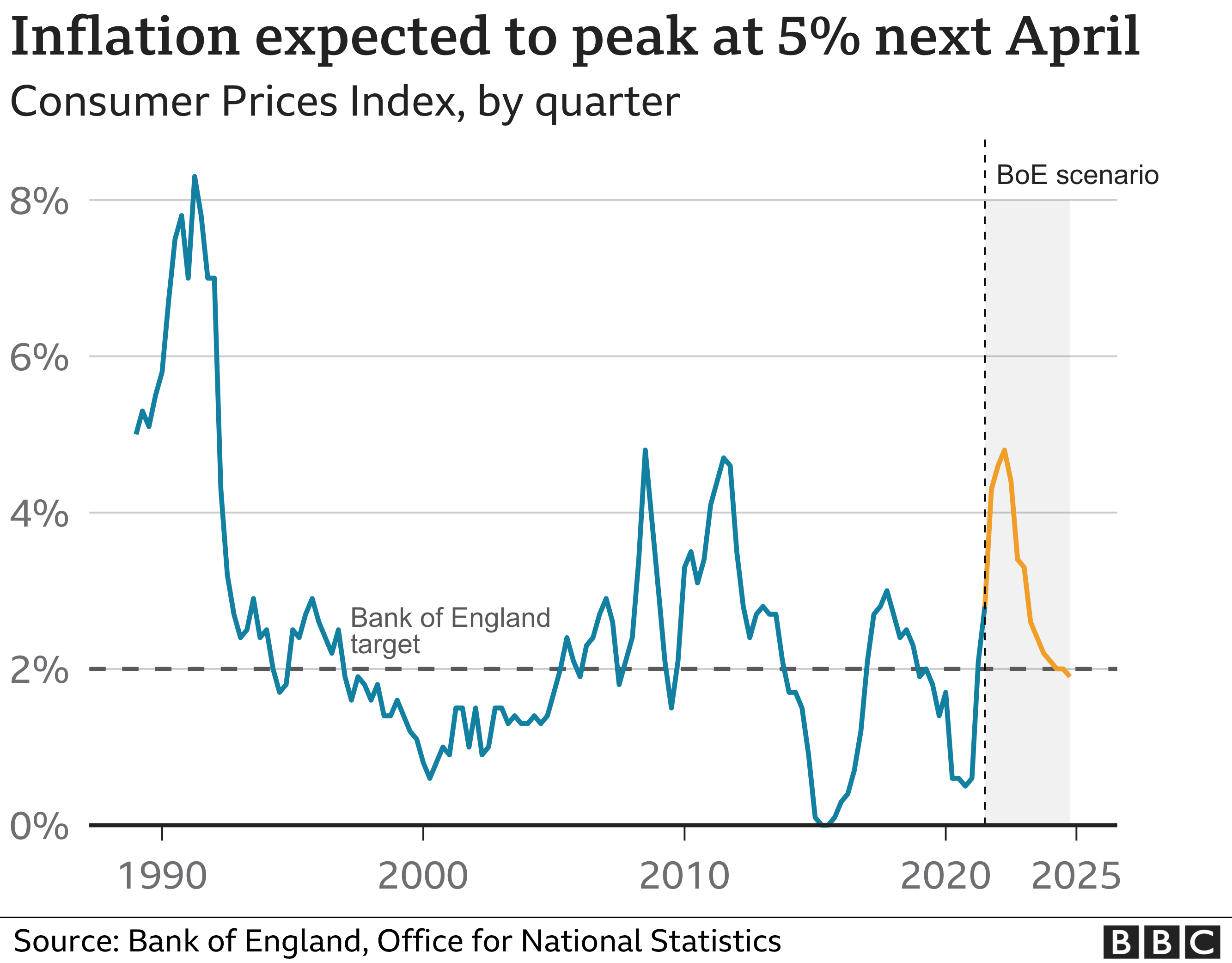
The global economy is a complex and dynamic system, constantly evolving under the influence of various factors. One of the most significant forces shaping economic realities is inflationary trends. While predicting the future with absolute certainty is impossible, understanding the potential drivers and implications of inflation in 2025 can provide valuable insights for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
Understanding Inflationary Trends
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. This means that the purchasing power of a given currency decreases as prices rise, requiring individuals to spend more to acquire the same goods or services.
Key Drivers of Inflationary Trends in 2025
Several factors could contribute to inflationary trends in 2025, each with its unique impact on the global economy:
1. Persistent Supply Chain Disruptions: The global supply chain has been grappling with disruptions since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. These disruptions have led to shortages of raw materials, components, and finished goods, pushing prices higher. While supply chains are gradually recovering, lingering bottlenecks and geopolitical tensions could continue to exert upward pressure on prices.
2. Energy Price Volatility: The global energy landscape is characterized by uncertainty, with geopolitical tensions and climate change policies impacting energy production and distribution. This volatility can translate into higher energy prices, affecting production costs and consumer expenses across various sectors.
3. Labor Market Dynamics: A tight labor market, characterized by high demand for workers and low unemployment, can lead to wage inflation. As businesses compete for talent, they may offer higher wages to attract and retain employees, contributing to rising prices.
4. Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies implemented by governments can influence inflation. Expansive fiscal policies, such as increased government spending, can stimulate demand and potentially lead to inflation. Similarly, loose monetary policies, such as low interest rates, can encourage borrowing and spending, contributing to inflationary pressures.
5. Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical tensions, including trade wars, sanctions, and conflicts, can disrupt global trade and supply chains, leading to price increases.
Impact of Inflationary Trends in 2025
Inflationary trends can have significant consequences for various stakeholders:
- Consumers: Rising prices erode purchasing power, forcing consumers to spend more on essential goods and services. This can lead to reduced consumption and a decline in living standards.
- Businesses: Inflation can increase production costs, making it challenging to maintain profit margins. Businesses may need to raise prices to compensate for higher input costs, potentially leading to a vicious cycle of inflation.
- Investors: Inflation can erode the value of investments, particularly those with fixed returns, such as bonds. Investors may need to adjust their portfolios to mitigate inflation risk.
- Governments: Inflation can lead to higher government spending on social programs and infrastructure projects, potentially increasing the national debt.
Strategies for Managing Inflation
Individuals, businesses, and governments can employ various strategies to mitigate the impact of inflation:
- Individuals: Diversify income sources, invest in assets that hedge against inflation, such as real estate or gold, and prioritize essential spending.
- Businesses: Increase productivity to offset rising costs, negotiate favorable contracts with suppliers, and consider passing on some cost increases to consumers.
- Governments: Implement policies to stabilize prices, such as controlling inflation through monetary policy and promoting competition in the market.
Related Searches
Understanding the potential impact of inflationary trends in 2025 requires exploring related concepts and factors:
- Inflationary Expectations: The expectations of future inflation can be self-fulfilling. If consumers and businesses anticipate high inflation, they may demand higher prices, contributing to an actual rise in inflation.
- Stagflation: This refers to a period of economic stagnation characterized by high inflation and low economic growth. Stagflation can be particularly challenging to manage, as traditional economic policies designed to combat inflation may exacerbate the recessionary pressures.
- Deflation: Deflation is the opposite of inflation, characterized by a sustained decrease in the general price level. While deflation might seem beneficial, it can lead to a vicious cycle of falling prices, reduced investment, and economic stagnation.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): This is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to inject liquidity into the economy by purchasing government bonds or other assets. QE can potentially lead to inflation if it is not managed carefully.
- Interest Rate Hikes: Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, which can slow economic growth and reduce inflationary pressures.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Building resilient supply chains is crucial for mitigating the impact of disruptions and price volatility. This involves diversifying suppliers, developing alternative sourcing strategies, and investing in technology to improve supply chain visibility.
- Green Inflation: This refers to the potential inflationary pressures associated with the transition to a low-carbon economy. As investments in renewable energy and sustainable technologies increase, the demand for critical materials like lithium and cobalt could rise, potentially leading to price increases.
FAQs about Inflationary Trends in 2025
Q: What are the main factors driving inflation in 2025?
A: The main drivers of inflation in 2025 are likely to include persistent supply chain disruptions, energy price volatility, tight labor markets, government policies, and geopolitical tensions.
Q: How will inflation impact consumers in 2025?
A: Inflation will erode consumer purchasing power, making it more expensive to buy essential goods and services. This could lead to reduced consumption and a decline in living standards.
Q: What steps can businesses take to mitigate the impact of inflation?
A: Businesses can increase productivity to offset rising costs, negotiate favorable contracts with suppliers, and consider passing on some cost increases to consumers.
Q: What role does government policy play in controlling inflation?
A: Governments can use monetary policy, such as adjusting interest rates, and fiscal policy, such as managing government spending, to influence inflation.
Q: What are the potential risks of high inflation?
A: High inflation can lead to economic instability, social unrest, and a decline in living standards. It can also erode the value of savings and investments.
Tips for Managing Inflationary Trends
- Monitor Inflation Rates: Stay informed about inflation trends by tracking consumer price indexes and other economic indicators.
- Diversify Investments: Consider diversifying your investment portfolio to include assets that hedge against inflation, such as real estate or gold.
- Budget Wisely: Create a detailed budget and prioritize essential spending.
- Negotiate with Suppliers: Businesses should negotiate favorable contracts with suppliers to mitigate the impact of rising input costs.
- Increase Productivity: Businesses should focus on improving efficiency and productivity to offset rising costs.
Conclusion
Inflationary trends in 2025 are likely to be influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including supply chain disruptions, energy price volatility, labor market dynamics, government policies, and geopolitical tensions. Understanding these drivers and their potential impact is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers to navigate the economic landscape effectively. By implementing appropriate strategies, such as diversifying investments, controlling spending, and promoting productivity, stakeholders can mitigate the negative consequences of inflation and ensure a more resilient and sustainable economy.
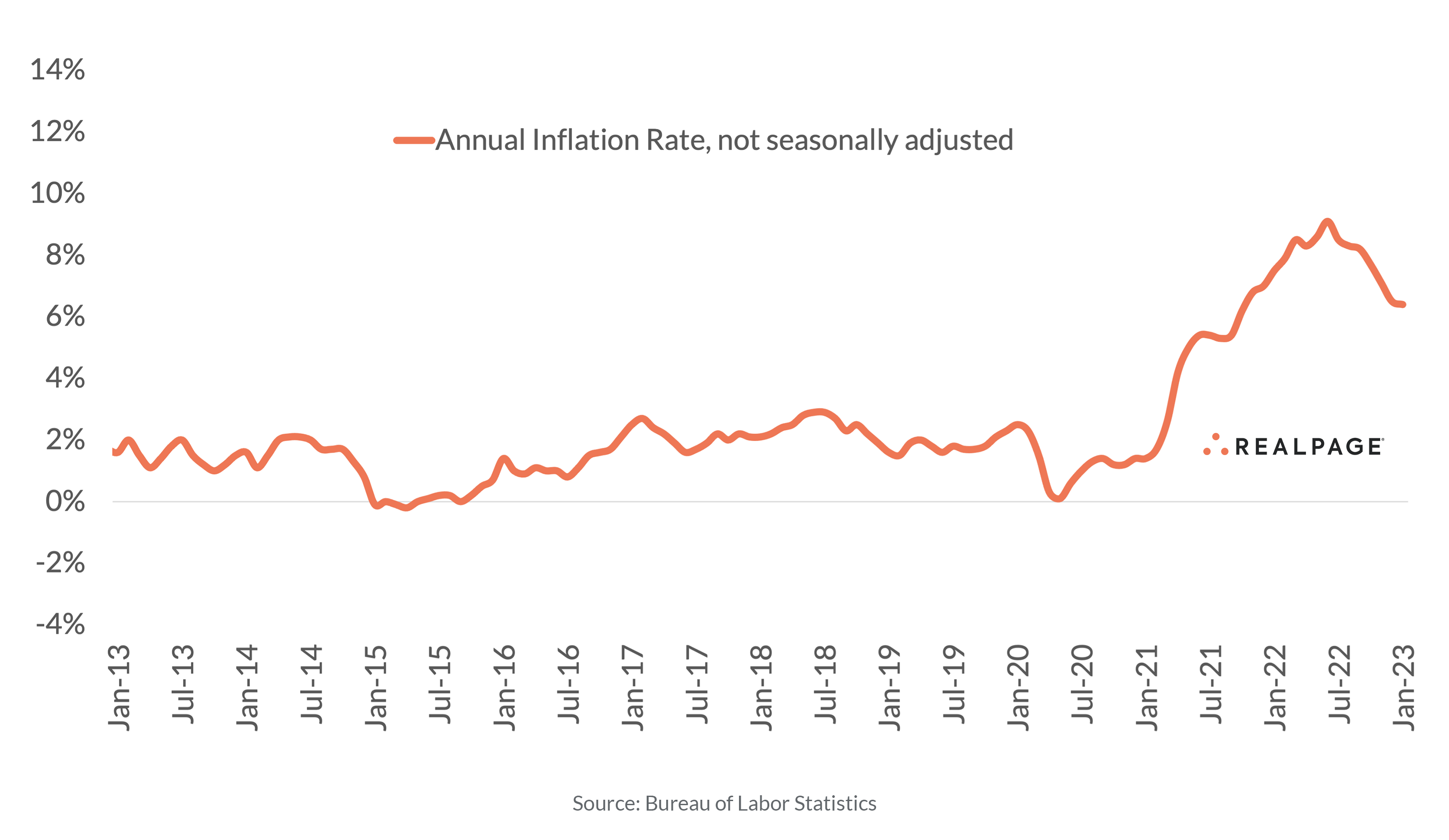
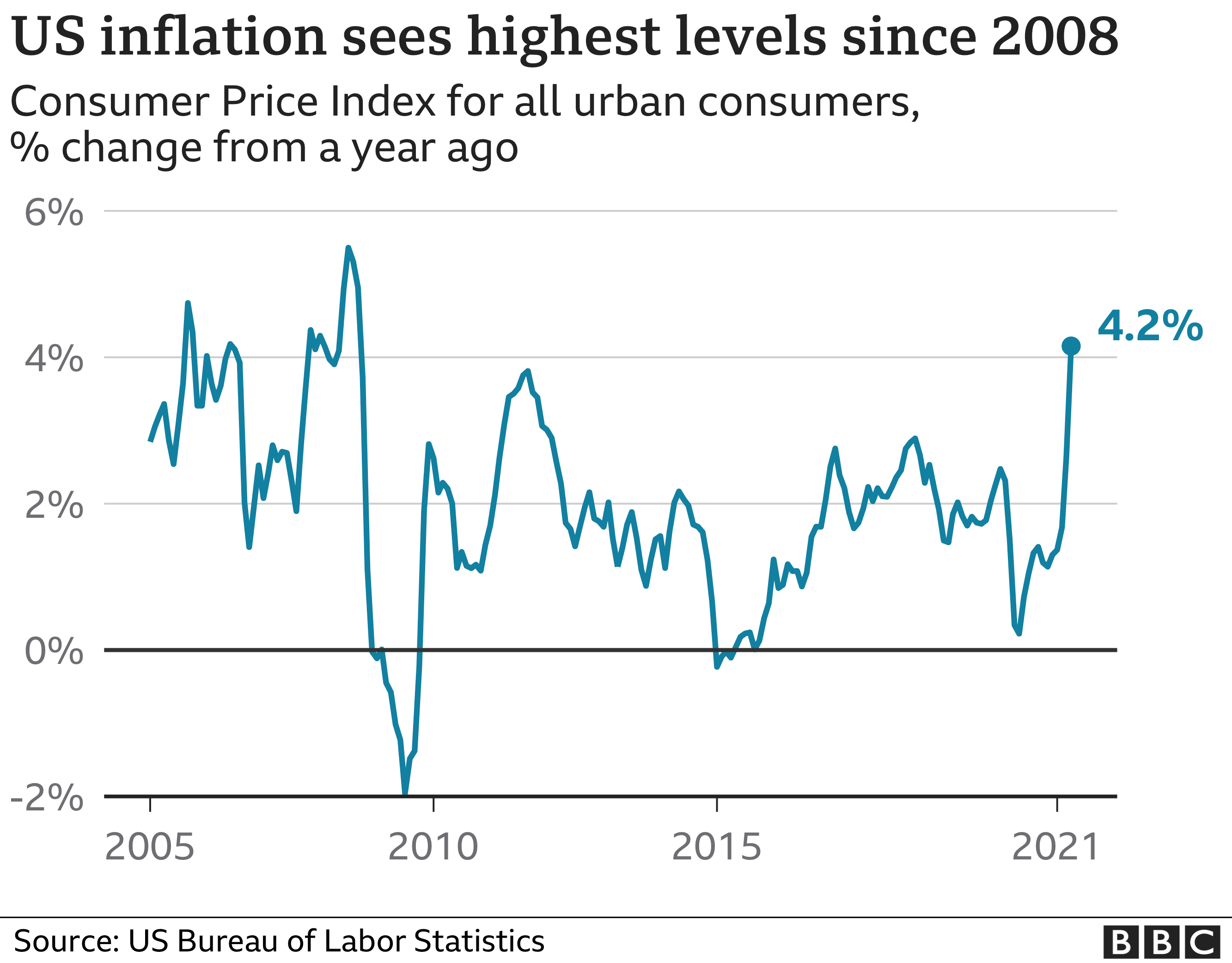





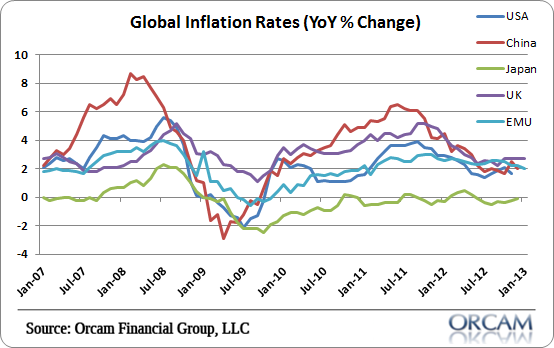
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Economic Landscape: A Look at Inflationary Trends in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!