Deciphering the Rising Tide: Two Trends Dominating Modern CO2 Concentration Charts
Deciphering the Rising Tide: Two Trends Dominating Modern CO2 Concentration Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Rising Tide: Two Trends Dominating Modern CO2 Concentration Charts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Rising Tide: Two Trends Dominating Modern CO2 Concentration Charts

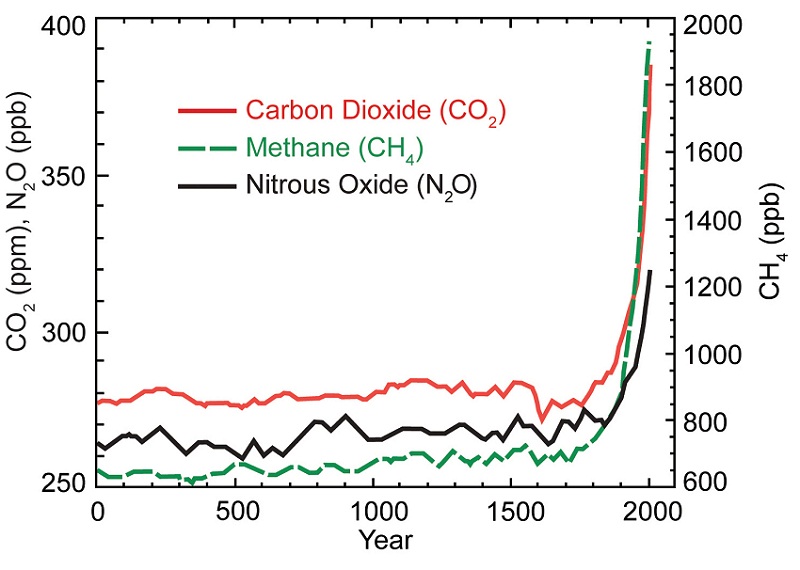
The Earth’s atmosphere is a delicate balance, and one of its most critical components is carbon dioxide (CO2). This colorless, odorless gas plays a vital role in regulating the planet’s temperature through the greenhouse effect. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly altered the natural CO2 cycle, leading to a dramatic increase in atmospheric concentrations.
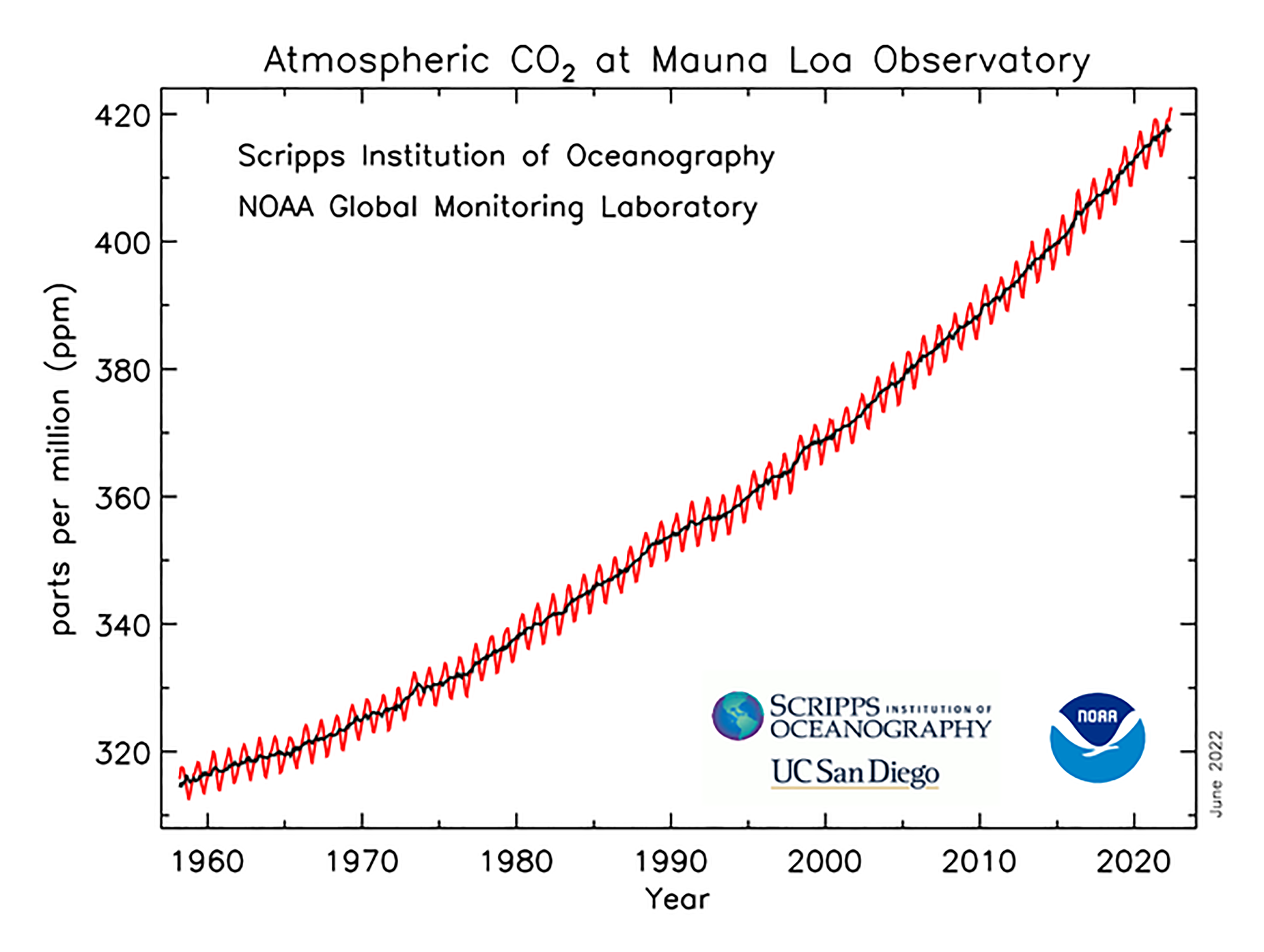
Analyzing modern monthly CO2 concentration charts reveals two prominent trends that underscore the urgency of addressing climate change:
1. A Steady and Unrelenting Rise:
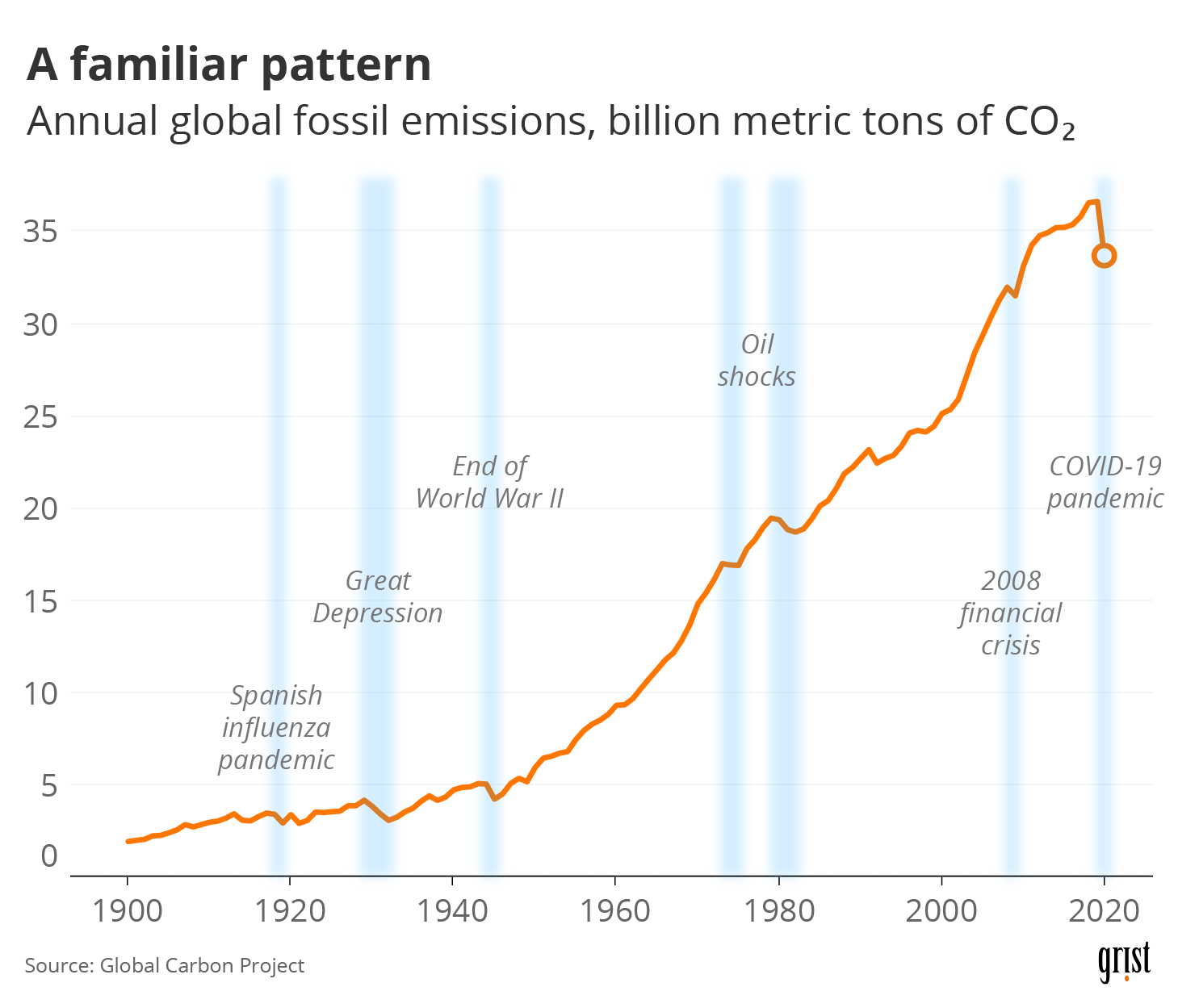
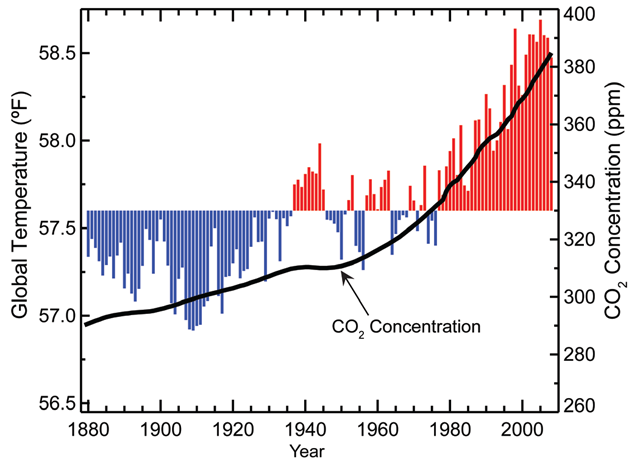
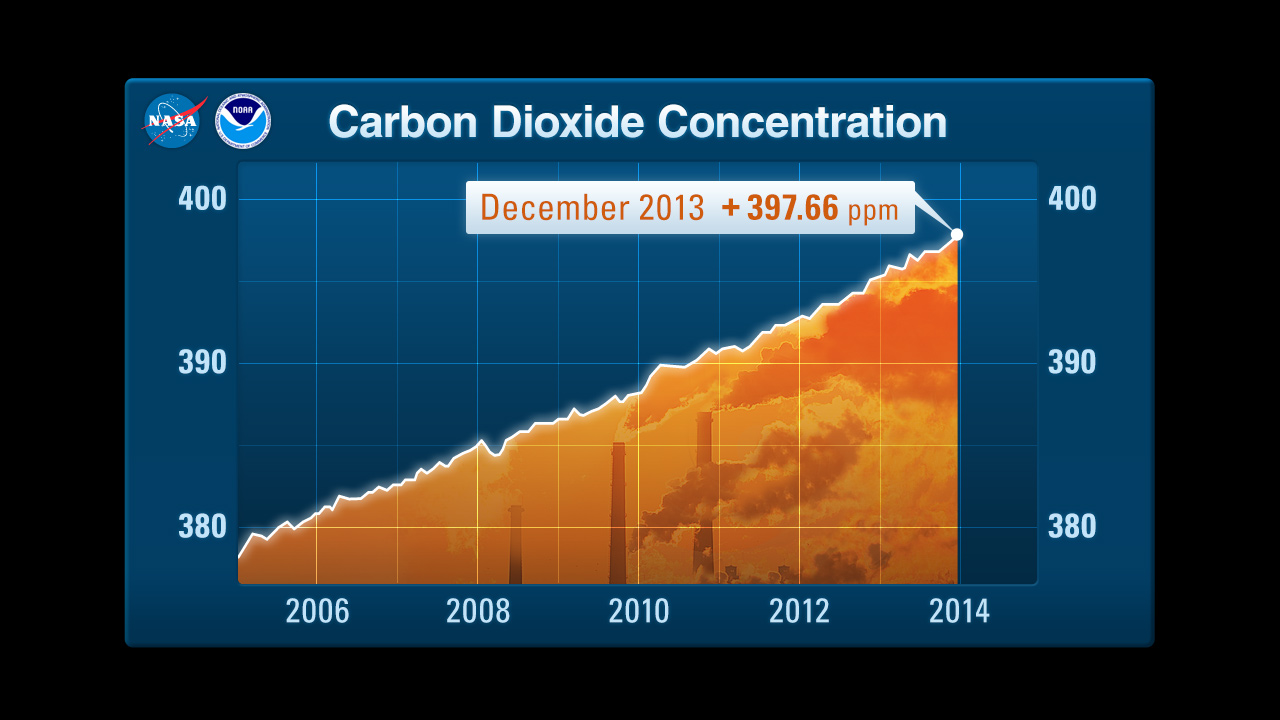
The most striking trend is the unwavering upward trajectory of CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere. This trend is evident across decades, with each year exceeding the previous year’s peak. The data paints a stark picture of a continuous accumulation of CO2, driving the greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming.
Understanding the Rise:
The relentless increase in CO2 levels is primarily attributed to the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes. These activities release vast quantities of CO2 into the atmosphere, far exceeding the natural absorption rates of the Earth’s ecosystems.
2. Seasonal Fluctuations:
While the overall trend is upward, the CO2 concentration charts also exhibit pronounced seasonal fluctuations throughout the year. These fluctuations are primarily driven by the photosynthetic activity of plants, which absorb CO2 during the growing season and release it during periods of dormancy.
Understanding the Fluctuations:
- Spring and Summer: During these months, plants actively photosynthesize, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to a dip in CO2 concentrations.
- Autumn and Winter: As plants enter dormancy, their photosynthetic activity declines, and CO2 release increases. This contributes to a rise in CO2 concentrations.
The Significance of These Trends:
The combination of a steady rise and seasonal fluctuations highlights the complex interplay between human activities and natural processes in shaping atmospheric CO2 levels. These trends serve as powerful indicators of the following:
- Accelerating Climate Change: The continuous increase in CO2 concentrations is a primary driver of climate change, leading to rising global temperatures, more extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
- The Need for Urgent Action: The trends in CO2 concentration charts underscore the urgency of transitioning to a low-carbon economy. Reducing emissions from fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources are crucial steps in mitigating the effects of climate change.
Exploring Related Searches:
1. CO2 Emissions by Country: Understanding which countries contribute the most to global CO2 emissions provides crucial insights into the global challenge.
2. CO2 Concentration Trends by Region: Analyzing regional variations in CO2 concentrations reveals the impact of local factors, such as deforestation and industrial activity.
3. CO2 Absorption by Forests: Forests play a vital role in absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Understanding the capacity of forests to sequester carbon is crucial for mitigating climate change.
4. CO2 Concentration and Ocean Acidification: Rising CO2 levels are impacting ocean chemistry, leading to acidification, which threatens marine ecosystems.
5. CO2 Concentration and Climate Feedback Loops: Changes in CO2 concentrations can trigger positive feedback loops, further accelerating climate change.
6. CO2 Concentration and Human Health: Elevated CO2 levels can have adverse effects on human health, particularly respiratory issues.
7. CO2 Concentration and Food Security: Climate change, driven by rising CO2 levels, can impact food production and contribute to food insecurity.
8. CO2 Concentration and Biodiversity Loss: Climate change, driven by rising CO2 levels, can lead to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
FAQs about CO2 Concentration Trends:
1. What is the current CO2 concentration in the atmosphere?
The current global average CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is above 420 parts per million (ppm).
2. How much has CO2 concentration increased since pre-industrial times?
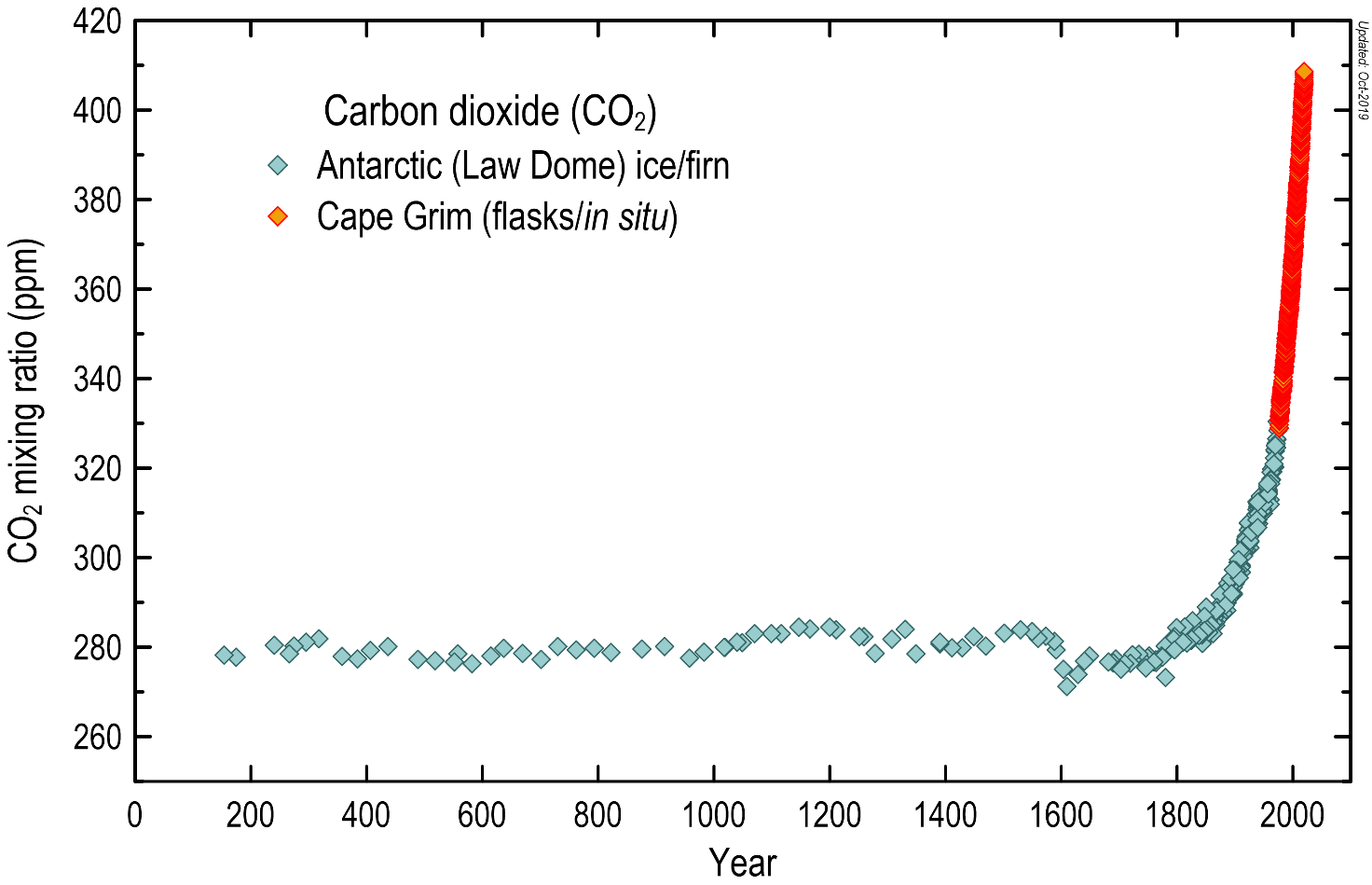
The global average CO2 concentration has increased by about 50% since pre-industrial times.
3. What is the role of natural processes in CO2 concentration?
Natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions and respiration, contribute to CO2 emissions, but human activities have significantly amplified these emissions.
4. What are the consequences of rising CO2 concentrations?
Rising CO2 concentrations contribute to global warming, sea level rise, more extreme weather events, and other environmental changes.
5. What can be done to reduce CO2 emissions?
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, promoting sustainable transportation, and protecting forests are crucial steps in reducing CO2 emissions.
Tips for Understanding CO2 Concentration Charts:
- Focus on the Overall Trend: Pay attention to the long-term upward trend in CO2 concentrations, even with seasonal fluctuations.
- Compare to Historical Data: Understanding how current CO2 levels compare to historical data provides valuable context.
- Consider Regional Variations: Explore regional differences in CO2 concentrations to understand the impact of local factors.
- Look for Correlations: Analyze correlations between CO2 concentrations and other environmental variables, such as temperature and sea level.
Conclusion:
The trends observed in modern monthly CO2 concentration charts paint a stark picture of the human impact on the Earth’s atmosphere. The steady increase in CO2 levels, coupled with seasonal fluctuations, underscores the urgent need for global action to mitigate climate change. By understanding these trends, we can better inform policy decisions, promote sustainable practices, and work towards a future where the Earth’s delicate balance is preserved for generations to come.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Rising Tide: Two Trends Dominating Modern CO2 Concentration Charts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!